The import-export business of fresh vegetables offers vast potential, especially for countries with strong agricultural bases like India. With increasing global demand for healthy, natural food products, fresh vegetables are in high demand in many parts of the world, including the UAE, UK, Malaysia, Qatar, and other countries with large Indian or health-conscious populations.
However, entering the fresh vegetable export market is not as simple as sending local produce abroad. It involves strict quality checks, cold chain management, and market research. If you want to build a successful and profitable fresh vegetable import-export business, here are three most important steps you must take:
Step 1: Ensure Quality and International Compliance

Quality is the backbone of the export business. International buyers have very specific requirements when it comes to the quality of fresh vegetables. They assess the color, size, freshness, shape, pesticide residue levels, and overall hygiene.
Here’s what you need to do:
- Source vegetables from certified farms: Always procure your vegetables from farms that follow GAP (Good Agricultural Practices). This ensures your produce is free from harmful chemicals and meets international food safety norms.
- Grading and sorting: Once harvested, vegetables must be properly sorted and graded based on size, ripeness, and appearance. Mixed or damaged produce can lead to rejection of the entire consignment.
- Laboratory testing: Conduct lab tests from NABL-accredited laboratories for pesticide residue, heavy metals, and other safety parameters. Many countries have strict Maximum Residue Limits (MRL) for different vegetables.
- Obtain export certifications: You will need a Phytosanitary Certificate from the Plant Quarantine Department, a Certificate of Origin, and an FSSAI license. For EU countries, you may also need GLOBALG.A.P. certification and traceability documentation.
Maintaining quality and compliance not only builds buyer confidence but also protects you from shipment rejections and financial losses.
Step 2: Post-Harvest Handling and Cold Chain Logistics
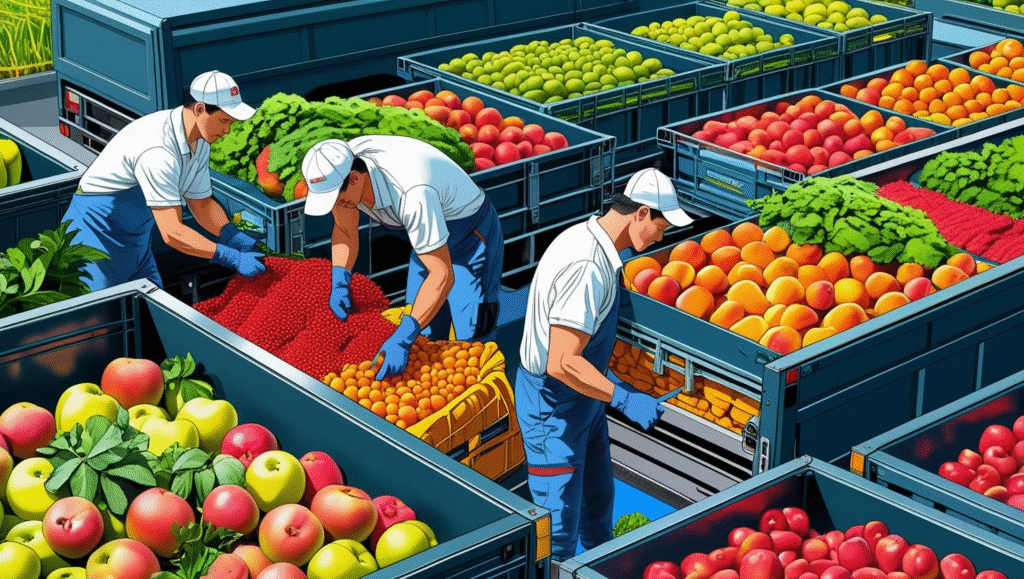
Fresh vegetables are highly perishable products. Poor handling can result in spoilage, wastage, and low customer satisfaction. Efficient post-harvest handling and cold chain logistics are essential to maintain freshness, texture, and shelf life.
Important points to focus on:
- Pre-cooling immediately after harvest: This helps remove field heat and slows down the respiration rate of vegetables. It is one of the first and most critical steps.
- Cold storage: After pre-cooling, vegetables must be stored in temperature-controlled storage facilities (usually between 4°C to 10°C, depending on the vegetable type).
- Packaging: Use export-grade packaging materials that allow ventilation and protect the vegetables during transit. Corrugated boxes with polyethylene liners are common.
- Reefer containers (refrigerated containers): For sea exports, use reefers with temperature and humidity control. For air freight, make sure to use insulated boxes and temperature-stable pallets.
- Transport logistics: Partner with professional Custom House Agents (CHAs) and freight forwarders who have experience in handling agri-exports. This ensures proper documentation, customs clearance, and smooth delivery.
Having an efficient cold chain system ensures that your vegetables arrive in the destination country fresh and ready for retail or distribution.
Step 3: Market Research and Finding Reliable Buyers
Knowing what to export, where to export, and who to export to is key to success in this business. Not every vegetable is in demand in every market. So market research is essential before entering any country or region.
Here’s how to get started:
- Identify high-demand vegetables: Popular export vegetables include okra (ladyfinger), bitter gourd, drumsticks, green chilies, curry leaves, ivy gourd (kundru/tondli), and fresh onions. Study import trends and preferences in your target countries.
- Understand buyer needs: Different buyers such as supermarkets, wholesalers, and importers have different packaging, quality, and volume requirements. Some may require 5 kg boxes, others may need 10 kg bulk packs.
- Find buyers through online platforms: Register on B2B portals like IndiaMART, TradeIndia, Alibaba, Global Sources, etc. Create a professional profile with product photos, specifications, and certifications.
- Use government resources: The APEDA (Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority) website provides export data, international exhibitions, buyer contacts, and export guidelines.
- Attend trade fairs and virtual expos: Participate in international trade shows to connect with genuine buyers and build your brand presence.
Building long-term relationships with reliable buyers ensures repeat business and consistent growth.
Conclusion
The fresh vegetable export business has tremendous potential if managed properly. By focusing on quality and compliance, cold chain and logistics, and market research and buyer connection, you can successfully establish your name in the global agri-export market.
Whether you’re an aspiring exporter or already doing small-scale trade, these three steps will help you take your business to the next level.
Meta Title:
3 Key Steps for Starting a Successful Fresh Vegetable Export Business
Meta Description:
Learn the 3 most important steps to succeed in the fresh vegetable import-export business, including quality compliance, cold chain logistics, and finding reliable buyers.
Discover the 3 most important steps to start and grow a successful fresh vegetable export business. In this blog, you’ll learn how to meet international quality standards, manage cold chain logistics effectively, and find reliable buyers in global markets.